| We are living in the high tech times. Technology and changing economy have changed the rules the way a business is done. Business organizations have to tune in to various markets and know the customers well. The successful companies are those who have been able to anticipate the customer need and innovate future products leveraging on technology. In a global as well as local scenario, customer holds the key to the growth of business and organizations. No wonder that when you open your mail box or your email, you are always flooded with marketing communication from all possible companies trying to build a relationship with you. Take a look at the cards in your wallet and you must be holding quite a few membership cards that make you feel privileged and keeping bringing rewards and prompting you to extend your relationship with them.
Relationship Marketing has never been more important for the Organizations as it has been now. In the field where competition is intense and life cycle of products and services is very small, customer relationship has emerged to be one of the key drivers to contribute a large chunk of sales revenue. When we talk of relationship marketing, we are not referring to customer service. Customer service refers to the quality of service on a transactional mode. By Relationship Marketing, we are referring to the level of Relationship that exists between the customer and the company. |
In terms of Relationship, there can be several ways of defining or measuring the quality of relationship with the Customer. Understanding of the depth of relationship and qualifying can help the Company in improving its reach to the markets as well as work towards increasing the depth of the relationship with the customer. In the first instance, we have a happy customer who has bought the product or a service and found it satisfactory.
When the Company reaches out to communicate with him and anticipate his future needs, he can be converted to a faithful customer. A faithful customer may be a repeat customer who does continues to buy the product from the company on repeat basis without making an effort to look at alternatives. However, at this stage the customer can be influenced and be vulnerable to competition as well as price sensitivity. Relationship marketing by the Company can help convert this customer from a faithful customer to a loyal customer. A loyal customer is one who has made an informed decision to go with the particular Company, is happy with the product, is loyal to the brand and is likely to advocate the same brand to friends and family because he believes in the Product as well as the Company and values the relationship. Apart from customer service, there are several marketing programmes and loyalty programmes besides brand advertising that the Companies carry out to build the relationship with the customer.
Relationship marketing gets translated and implemented through the marketing strategies, promotional programs as well as through marketing communication programs. When implemented as a part of marketing strategy, the relationship is normally focussed on leveraging the brands and products of the Company with the customer. Besides the marketing activities, the Companies implement internal and external corporate communications too keeping in view the Customers.
Marketing strategies are required to define the relationship marketing strategies for each of the product or service category taking into account the geographies, the customer profile as well as the overall RM objective of the Company. The RM strategy in case of a product company would be different from that of a service company and the element of communication design strategy would need to be different for a product from that of a service. In case of a product, the Customer is likely to respond in terms of brand, tangible and quantifiable performance of the product and the satisfaction derived from post sales service. In case of service, however, there is no tangible product and the customer’s expectations are different when it comes to service that is mainly concentrated around his perceptions and experience.
Therefore understanding the concept of Relationship marketing, the difference between RM and Customer Service as well as the ways and means of implementing or achieving RM objectives through effective marketing strategies is important for all the marketing managers and students who are going to be the drivers to defining, planning, detailing and implementing marketing strategies. An effective Marketing Manager should be able to effectively design marketing policies and strategies that are aligned with the Company’s RM objective and help build the relationship between the Company and Customer, Partners as well as the intermediaries who are critical to one’s business.
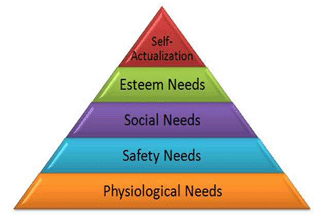 FIGURE: Maslow’s Need Hierarchy Model
FIGURE: Maslow’s Need Hierarchy Model


